Product Information
Linear guides, also known as linear rails or slide rails, are precision transmission components used to achieve linear reciprocating motion.
The following is a detailed introduction:
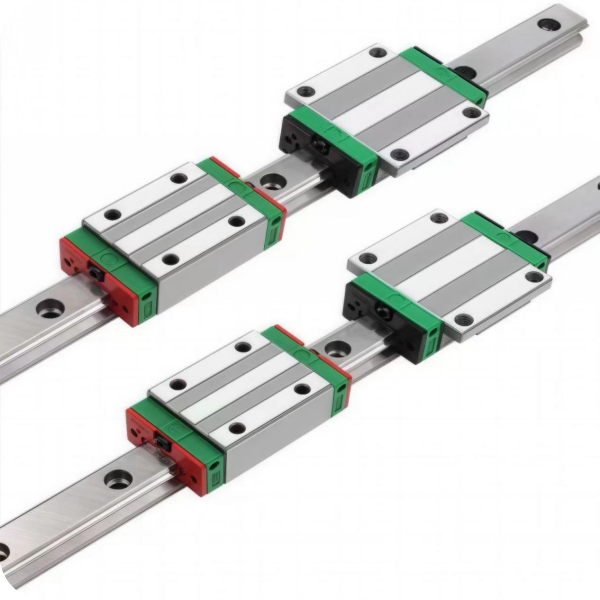
- Basic Structure: Typically consists of a rail, slider, rolling elements, retainer, recirculation system, and end caps. The rolling elements are usually balls or rollers, which circulate within a closed raceway between the slider and the rail.
- Working Principle: It can be understood as a rolling guide. Steel balls roll continuously between the slider and the rail, enabling the load platform to achieve high-precision linear motion along the rail, reducing the friction coefficient to about one-fiftieth of that of traditional sliding guides.
- Performance Characteristics: Features high precision and high rigidity. Preloading technology can eliminate clearance and improve rigidity; the friction coefficient is extremely low, making it suitable for high-speed motion; the rolling contact surface has minimal wear and a long material fatigue life; the contact angle of each ball row is usually 45°, giving the slider the same rated load capacity in all four directions and allowing it to withstand a certain torque load; as a standardized component, it is easy to install, and the sliders and rails of many brands can be replaced individually, offering good interchangeability.
- Types: Can be classified by load into miniature guides, medium-load guides, and heavy-load guides; by slider form into standard type, widened type, lengthened type, short type, etc.; and by special functions into self-lubricating, high dustproof, high-temperature resistant types, etc.
- Application Fields: Widely used in CNC machine tools, industrial automation equipment, precision measuring instruments, semiconductor and electronic manufacturing equipment, medical equipment, and other fields. For example, the spindle feed of machining centers, the arm movement of robots, the probe movement of coordinate measuring machines, and the workpiece stage movement of lithography machines all rely on linear guides to ensure accuracy and stability.
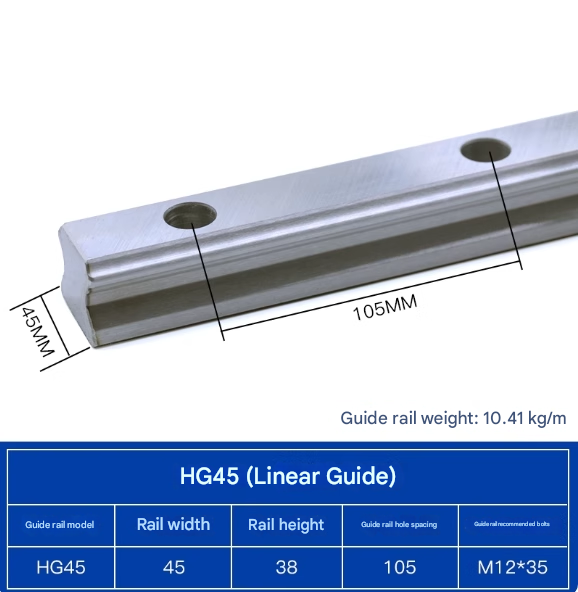
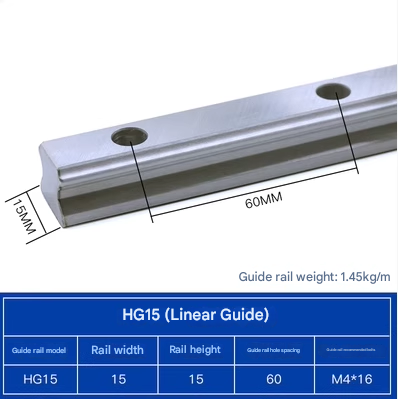
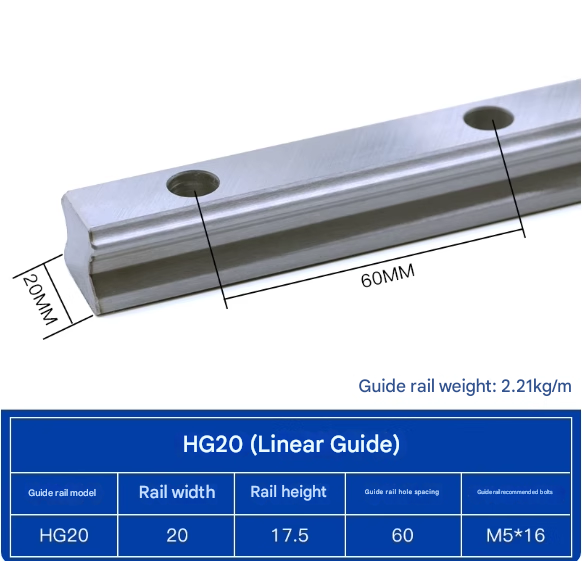
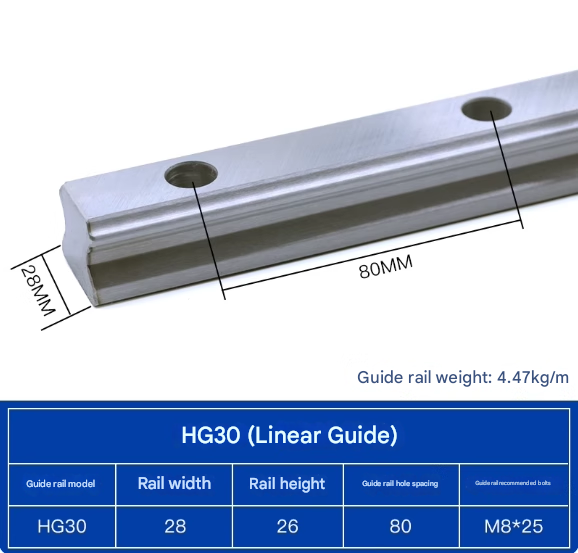
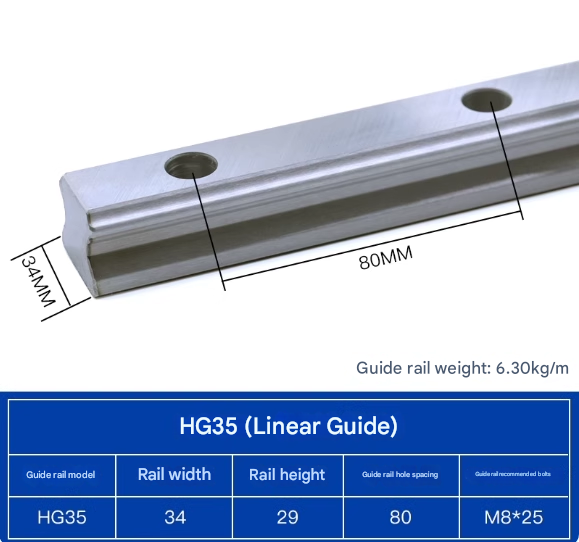
Product Specifications